Which statements correctly describe epithelial tissue – Epithelial tissue, a fundamental component of the human body, plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis and protecting against external threats. This article delves into the defining features, functions, and clinical significance of epithelial tissue, providing a comprehensive understanding of its essential nature.
Characteristics of Epithelial Tissue: Which Statements Correctly Describe Epithelial Tissue
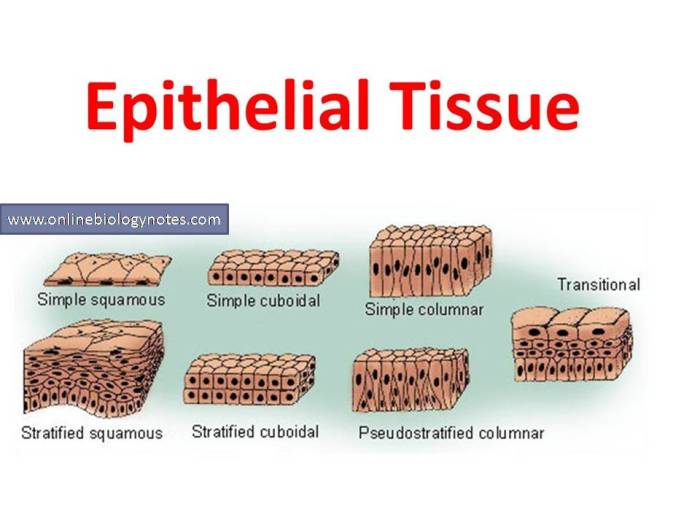
Epithelial tissue is a type of tissue that covers the surfaces of the body and lines the internal organs and cavities. It is composed of closely packed cells that form a protective barrier between the body and its surroundings. Epithelial cells are also responsible for absorption, secretion, and sensation.Epithelial
tissue is characterized by the following features:
- It is composed of cells that are closely packed together.
- The cells are arranged in one or more layers.
- The cells are polarized, meaning that they have a distinct apical (top) and basal (bottom) surface.
- The apical surface is exposed to the environment, while the basal surface is attached to the underlying connective tissue.
There are different types of epithelial cells, each with its own unique structure and function. Some of the most common types of epithelial cells include:
- Squamous cells are thin, flattened cells that are found in areas where there is a need for diffusion or filtration.
- Cuboidal cells are cube-shaped cells that are found in areas where there is a need for both absorption and secretion.
- Columnar cells are tall, column-shaped cells that are found in areas where there is a need for absorption or secretion.
- Goblet cells are specialized columnar cells that produce and secrete mucus.
Epithelial tissue is found in a variety of locations throughout the human body, including the skin, the lining of the digestive tract, the lining of the respiratory tract, and the lining of the urinary tract.
Functions of Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial tissue performs a variety of important functions, including:
- Protection: Epithelial tissue protects the body from the environment by forming a physical barrier between the body and its surroundings.
- Absorption: Epithelial tissue absorbs nutrients from the environment and transports them to the bloodstream.
- Secretion: Epithelial tissue secretes hormones, enzymes, and other substances into the bloodstream or into the environment.
- Sensing and responding to stimuli: Epithelial tissue contains sensory receptors that can detect changes in the environment and trigger appropriate responses.
Organization of Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial tissue is organized into layers, with the number of layers varying depending on the location and function of the tissue. The most common types of epithelial tissue are simple epithelium, which is composed of a single layer of cells, and stratified epithelium, which is composed of multiple layers of cells.The
basement membrane is a thin layer of connective tissue that separates the epithelial tissue from the underlying connective tissue. The basement membrane provides support and nourishment to the epithelial tissue.The organization of epithelial tissue is influenced by a number of factors, including the function of the tissue, the location of the tissue, and the developmental stage of the organism.
Development and Differentiation of Epithelial Tissue
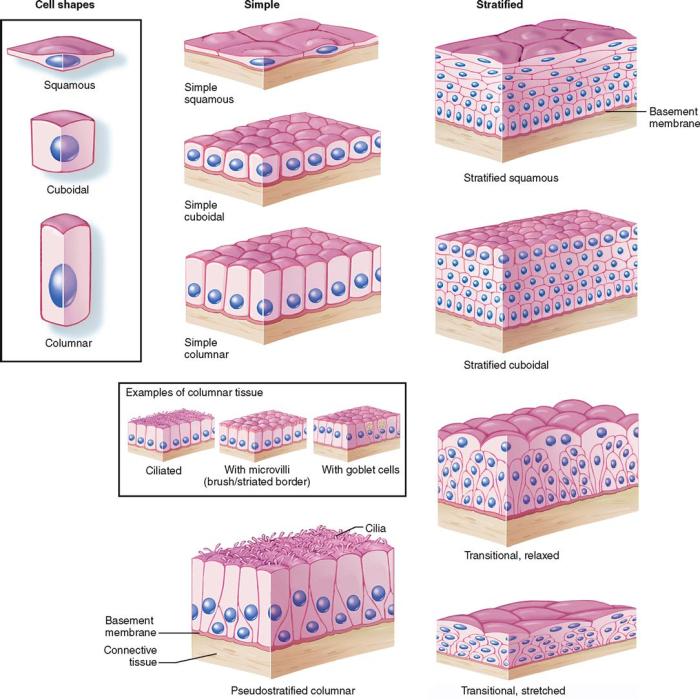
Epithelial tissue originates from the three germ layers during embryonic development. The ectoderm gives rise to the epidermis, the lining of the mouth and anus, and the sensory receptors. The mesoderm gives rise to the lining of the digestive tract, the lining of the respiratory tract, and the lining of the urinary tract.
The endoderm gives rise to the lining of the digestive tract and the lining of the respiratory tract.Epithelial cells differentiate into their specific types through a process called epithelial differentiation. Epithelial differentiation is controlled by a number of factors, including genetic factors, environmental factors, and cell-cell interactions.
Clinical Significance of Epithelial Tissue
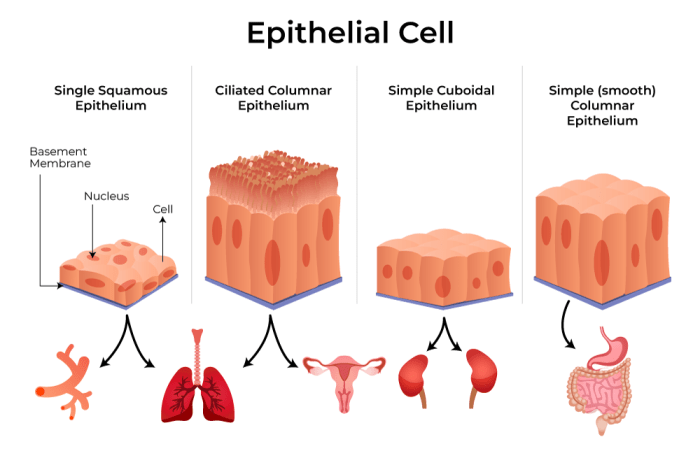
Epithelial tissue is involved in a number of diseases, including cancer, infections, and autoimmune diseases. Cancer is a disease in which epithelial cells grow out of control and form tumors. Infections are caused by microorganisms that invade and damage epithelial tissue.
Autoimmune diseases are diseases in which the immune system attacks and damages epithelial tissue.Epithelial tissue is also used in tissue engineering, which is the process of creating new tissue from living cells. Tissue engineering is used to repair damaged tissue and to create new organs.
FAQ
What is the primary function of epithelial tissue?
Protection and regulation of the internal environment.
What are the three main types of epithelial cells?
Squamous, cuboidal, and columnar.
Where is epithelial tissue commonly found in the human body?
Skin, lining of organs and cavities, and glands.