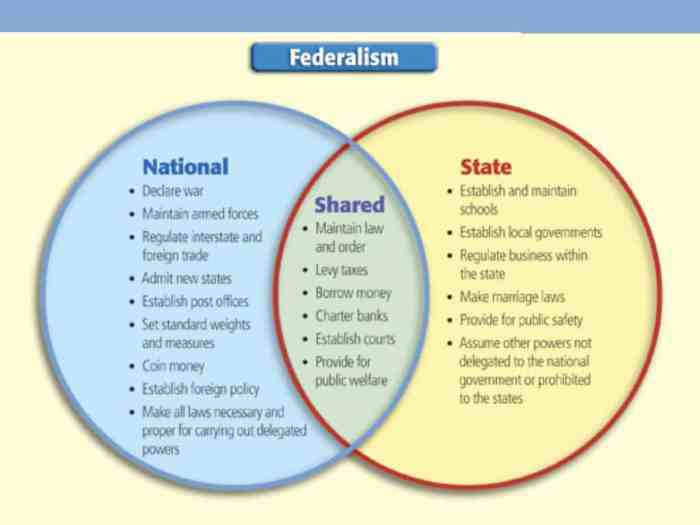
The federal in federalism venn diagram is a conceptual framework that illustrates the division of powers between the federal and state governments in the United States. This diagram serves as a valuable tool for understanding the complex relationship between these two levels of government and their respective roles in shaping American society.
The federal government is responsible for matters of national importance, such as foreign policy, defense, and interstate commerce. State governments, on the other hand, are responsible for matters of local concern, such as education, healthcare, and public safety. However, there is a significant overlap between the powers of the federal and state governments, as both levels of government share certain responsibilities, such as taxation and law enforcement.
1. Historical Context of Federalism in the United States
Federalism, a system of government in which power is divided between a central authority and constituent political units, has its roots in the American experience. The Articles of Confederation, ratified in 1781, established a loose confederation of states with limited central authority.
However, the inherent weaknesses of this system led to the Constitutional Convention in 1787, which produced the U.S. Constitution.
Division of Powers
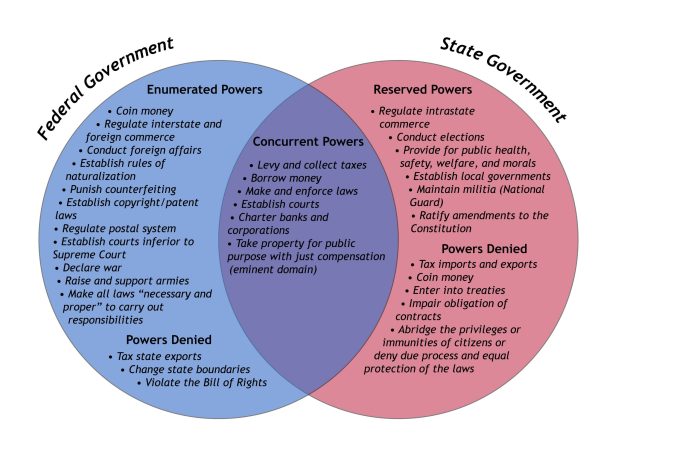
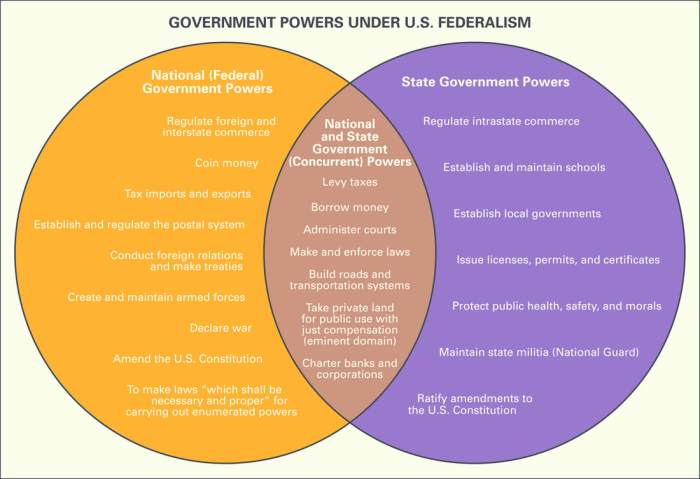
The Constitution created a more robust federal system, dividing powers between the federal and state governments. The federal government was granted exclusive powers over foreign affairs, defense, interstate commerce, and other matters of national importance. The states retained all other powers, known as reserved powers.
Evolution of Federalism
Federalism in the United States has evolved over time, with the balance of power between the federal and state governments shifting in response to historical events and societal changes. The Civil War, for example, strengthened the federal government’s authority, while the New Deal era saw an expansion of federal power in economic and social policy.
2. The Role of the Federal Government in Federalism
Key Responsibilities and Powers
- Foreign policy and diplomacy
- National defense and security
- Regulation of interstate commerce
- Taxation and fiscal policy
- Enforcement of federal laws
Interaction with State and Local Governments
The federal government interacts with state and local governments through various mechanisms, including grants, cooperative agreements, and cross-jurisdictional partnerships. It also has the authority to preempt state laws in certain areas.
Implied Powers
The Constitution’s “necessary and proper” clause has allowed the federal government to expand its powers beyond those explicitly enumerated in the document. This concept of implied powers has been used to justify a wide range of federal actions, including the establishment of national banks and the regulation of the Internet.
3. The Role of State Governments in Federalism
Key Responsibilities and Powers
- Education
- Law enforcement and criminal justice
- Public health and safety
- Transportation and infrastructure
- Regulation of intrastate commerce
Interaction with the Federal Government and Local Governments, The federal in federalism venn diagram
State governments interact with the federal government through various mechanisms, including grants, cooperative agreements, and the representation of state interests in Congress. They also have the authority to regulate local governments within their borders.
Reserved Powers
The Constitution’s Tenth Amendment reserves all powers not delegated to the federal government to the states. This concept of reserved powers has protected the autonomy of state governments and allowed them to address local issues and needs.
4. The Relationship Between Federal and State Governments
Cooperation and Conflict
The relationship between federal and state governments is characterized by both cooperation and conflict. They often work together on issues of mutual concern, such as infrastructure development and disaster relief. However, conflicts can arise when federal policies conflict with state interests or when states resist federal mandates.
Dispute Resolution Mechanisms
Various mechanisms exist for resolving disputes between federal and state governments, including litigation, negotiation, and intergovernmental agreements. The Supreme Court plays a significant role in interpreting the Constitution and resolving federal-state conflicts.
Facilitation of Cooperation and Innovation
Federalism has facilitated cooperation and innovation between states. By providing a framework for collaboration, it has allowed states to share best practices, develop joint initiatives, and address regional challenges.
5. The Impact of Federalism on American Society
Positive Impacts
- Protects individual rights and liberties
- Promotes diversity and local autonomy
- Encourages innovation and experimentation
- Facilitates cooperation and problem-solving
Negative Impacts
- Can lead to conflicts between federal and state governments
- May limit the ability of the federal government to address national issues
- Can create disparities in public services and policies across states
Shaping American Society
Federalism has profoundly shaped American society. It has contributed to the country’s unique blend of unity and diversity, fostered a spirit of innovation and experimentation, and protected the rights and liberties of individuals.
Q&A: The Federal In Federalism Venn Diagram
What is federalism?
Federalism is a system of government in which power is divided between a central government and several regional governments.
What are the advantages of federalism?
Federalism allows for a more efficient and responsive government, as well as greater protection for individual rights.
What are the disadvantages of federalism?
Federalism can lead to conflict between the central and regional governments, as well as a lack of coordination in policymaking.