Compared to 37k the isotope 42k has a – Potassium isotopes, particularly 37K and 42K, exhibit distinct properties that have led to their diverse applications in various fields. Compared to 37K, the isotope 42K possesses a higher mass number and a shorter half-life, resulting in a lower relative abundance.
This article delves into the unique characteristics and applications of 42K, exploring its significance in geological dating, medical imaging, and environmental studies.
The contrasting properties of 37K and 42K stem from their differing neutron counts, which influence their radioactive decay rates and subsequent abundance in nature. These isotopes serve as valuable tools for scientific investigations, providing insights into the age of rocks, the distribution of potassium in the body, and the movement of groundwater.
Potassium Isotopes
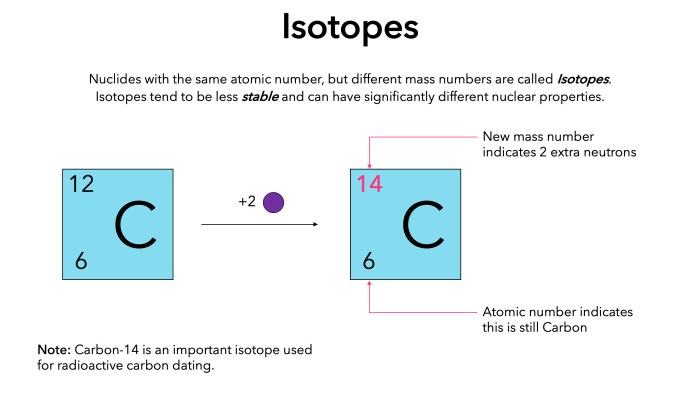
Potassium has several naturally occurring isotopes, with atomic numbers 19 and varying mass numbers. The most common isotopes of potassium are 37K, 40K, and 42K. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons, resulting in different mass numbers.
| Isotope | Atomic Number | Mass Number | Relative Abundance (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 37K | 19 | 37 | 93.2581 |
| 40K | 19 | 40 | 0.0117 |
| 42K | 19 | 42 | 6.7302 |
Radioactive Decay: Compared To 37k The Isotope 42k Has A

K is a radioactive isotope that undergoes beta decay, emitting an electron and an antineutrino and transforming into 42Ca. This radioactive decay process has a half-life of 12.4 billion years, meaning that it takes 12.4 billion years for half of the 42K atoms in a sample to decay.
The abundance of 42K is significantly lower than 37K due to its radioactive decay over time.
Applications of Potassium Isotopes, Compared to 37k the isotope 42k has a
Potassium isotopes are widely used in geological dating methods, such as potassium-argon dating. By measuring the abundance of 40K and 42K in rocks and minerals, scientists can determine their age. This technique is particularly useful for dating volcanic rocks and sedimentary rocks.Potassium
isotopes also have applications in medical imaging, specifically in positron emission tomography (PET). PET involves injecting a small amount of radioactive tracer, often containing 42K, into the body. The decay of 42K emits positrons, which then interact with electrons in the body, releasing gamma rays that can be detected by scanners to create images of metabolic activity.
Environmental Applications
Potassium isotopes are used in environmental studies to trace the movement of groundwater and understand the interactions between water and soil. By measuring the abundance of 42K in groundwater samples, scientists can track its flow and determine the age of the water.
This information is crucial for managing water resources and assessing groundwater contamination.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the primary difference between 37K and 42K?
The primary difference lies in their neutron counts, which result in varying radioactive decay rates and abundances.
How is 42K used in geological dating?
The decay of 42K to 40Ar is utilized in potassium-argon dating, providing estimates of the age of rocks and minerals.
What is the significance of 42K in medical imaging?
42K is used in positron emission tomography (PET) to track the distribution of potassium in the body, aiding in the diagnosis and monitoring of various medical conditions.