Embark on an educational journey with our comprehensive guide to sickle cell anemia NClex questions. Delve into the intricacies of this condition, exploring its pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, management, and nursing care. Prepare yourself for success in your nursing exams and gain invaluable knowledge to enhance patient outcomes.
Sickle cell anemia, a prevalent inherited blood disorder, presents unique challenges in healthcare. This guide equips you with the essential knowledge to navigate the complexities of this condition, ensuring optimal patient care.
Pathophysiology of Sickle Cell Anemia: Sickle Cell Anemia Nclex Questions
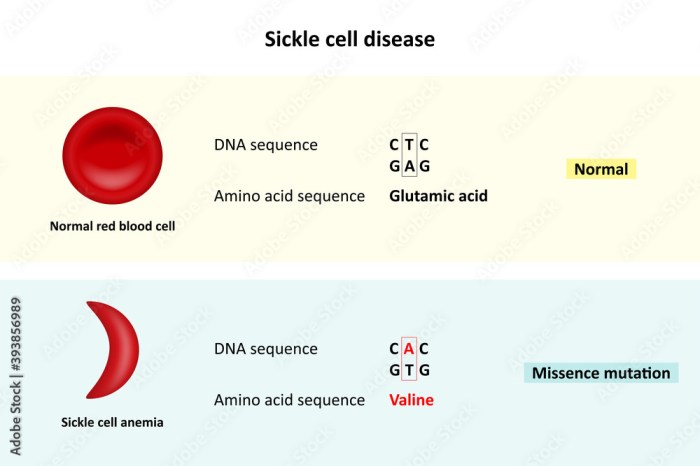
Sickle cell anemia is an inherited blood disorder caused by a mutation in the beta-globin gene. This mutation results in the production of abnormal hemoglobin, called sickle hemoglobin (HbS), which is prone to polymerization under certain conditions.
Structural Abnormalities of Sickle Hemoglobin
HbS differs from normal hemoglobin (HbA) by a single amino acid substitution at position 6 of the beta-globin chain. This substitution, glutamic acid for valine, causes the hemoglobin molecule to become less soluble and more prone to polymerization.
Pathophysiology of Sickle Cell Crisis
Under conditions of low oxygen tension, HbS molecules polymerize, forming long, rigid fibers within red blood cells. These fibers distort the shape of the red blood cells, making them sickle-shaped. Sickled red blood cells are less flexible and can become trapped in small blood vessels, blocking blood flow and causing tissue ischemia.
Clinical Manifestations of Sickle Cell Anemia
The clinical manifestations of sickle cell anemia vary widely and depend on the severity of the disease. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Chronic anemia
- Painful episodes (crises)
- Splenomegaly
- Jaundice
- Delayed growth and puberty
- Frequent infections
Types of Pain Crises
Pain crises are a hallmark of sickle cell anemia. They are characterized by severe pain in various parts of the body, including the bones, abdomen, and chest.
- Vaso-occlusive crisis:The most common type of pain crisis, caused by blockage of blood vessels by sickled red blood cells.
- Aplastic crisis:A sudden drop in red blood cell production, leading to severe anemia.
- Sequestration crisis:Trapping of red blood cells in the spleen, causing sudden enlargement of the spleen and a drop in hemoglobin levels.
Complications of Sickle Cell Anemia, Sickle cell anemia nclex questions
Sickle cell anemia can lead to various complications, including:
- Stroke
- Organ damage (e.g., kidney, liver, heart)
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Increased risk of infection
Diagnosis and Management of Sickle Cell Anemia
Sickle cell anemia is typically diagnosed through a blood test that identifies the presence of HbS. Other tests may include:
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Hemoglobin electrophoresis
- Genetic testing
The management of sickle cell anemia focuses on preventing and treating complications. Key principles include:
- Hydration:Adequate hydration helps prevent sickling.
- Pain management:Medications such as opioids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are used to relieve pain.
- Blood transfusions:Transfusions can be used to raise hemoglobin levels and prevent complications.
- Hydroxyurea:A medication that reduces the production of HbS and improves blood flow.
- Stem cell transplant:A potentially curative treatment for sickle cell anemia.
Nursing Care for Patients with Sickle Cell Anemia
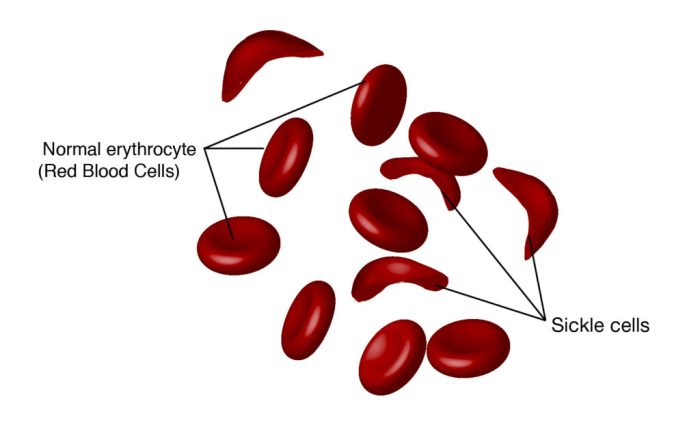
Nursing care for patients with sickle cell anemia focuses on:
Nursing Assessments
- Pain assessment
- Vital signs monitoring
- Hydration status assessment
- Neurological assessment
Nursing Interventions
- Managing pain:Administering medications, providing comfort measures, and educating patients on pain management techniques.
- Preventing complications:Encouraging hydration, promoting infection control, and monitoring for signs of complications.
- Providing emotional support:Providing empathy, understanding, and resources to support patients and their families.
Patient Education and Adherence
Patient education is crucial for managing sickle cell anemia. Nurses should educate patients on:
- The nature of the disease
- Importance of hydration and pain management
- Signs and symptoms of complications
- Importance of adherence to treatment plans
FAQ Compilation
What is the genetic basis of sickle cell anemia?
Sickle cell anemia is caused by a mutation in the beta-globin gene, which leads to the production of abnormal hemoglobin (hemoglobin S) that polymerizes under low oxygen conditions, causing red blood cells to assume a sickle shape.
What are the common signs and symptoms of sickle cell anemia?
Common signs and symptoms include episodes of severe pain (pain crises), anemia, fatigue, shortness of breath, jaundice, and increased susceptibility to infections.
What is the role of hydroxyurea in the treatment of sickle cell anemia?
Hydroxyurea is a medication that helps prevent the sickling of red blood cells, thereby reducing the frequency and severity of pain crises and other complications.