Beginning with the geology rocks equations answer key, this discourse embarks on a captivating exploration of the Earth’s very essence, revealing the processes that shape and mold our planet’s rocky foundations.
Through a comprehensive examination of geological processes, rock classification, properties, and structures, this narrative unravels the intricate tapestry of Earth’s geological history, empowering readers with a profound understanding of the forces that have shaped our planet over eons.
Geological Processes
Geological processes are the natural forces that shape and alter the Earth’s surface and crust. These processes include weathering, erosion, deposition, and tectonic activity.
Weathering is the breakdown of rocks and minerals at or near the Earth’s surface. Erosion is the transport of weathered material away from its original location. Deposition is the accumulation of eroded material in a new location. Tectonic activity is the movement of the Earth’s crust, which can create mountains, valleys, and other landforms.
Rock Classification
Rocks are classified into three main types based on their composition and texture: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic.
Igneous rocks are formed from the cooling and solidification of molten rock (magma or lava). Sedimentary rocks are formed from the accumulation and cementation of sediments, such as sand, silt, and clay. Metamorphic rocks are formed when existing rocks are subjected to high heat and pressure.
| Rock Type | Composition | Texture |
|---|---|---|
| Igneous | Formed from cooled magma or lava | Crystalline or glassy |
| Sedimentary | Formed from accumulated sediments | Clastic, chemical, or organic |
| Metamorphic | Formed from existing rocks under heat and pressure | Foliated or non-foliated |
Rock Properties: Geology Rocks Equations Answer Key
The physical and chemical properties of rocks influence their behavior and use. These properties include density, porosity, and permeability.
Density is the mass of a rock per unit volume. Porosity is the percentage of a rock’s volume that is occupied by pores (empty spaces). Permeability is the ability of a rock to allow fluids to flow through it.
These properties are important in geological applications, such as groundwater flow modeling, oil and gas exploration, and engineering design.
Rock Structures
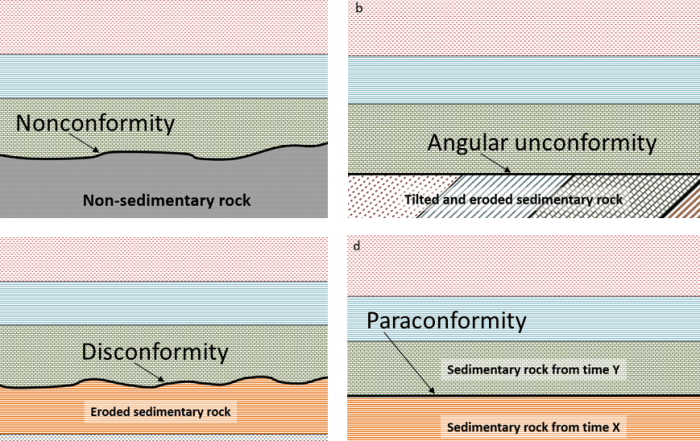
Rocks can exhibit a variety of structures, including folds, faults, and joints.
Folds are bends or curves in rock layers. Faults are fractures in rock along which movement has occurred. Joints are fractures in rock that have not experienced movement.
These structures can provide information about the geological history of an area and can impact the behavior of groundwater and other fluids.
| Structure Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Fold | Bend or curve in rock layers |
| Fault | Fracture in rock with movement |
| Joint | Fracture in rock without movement |
Rock Equations
A number of equations are commonly used in geology to calculate rock properties and relationships.
The following table summarizes some of the most important equations:
| Equation | Variables | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Density = mass / volume | Density (g/cm3), mass (g), volume (cm3) | Calculate the density of a rock |
| Porosity = (volume of pores / total volume) x 100 | Porosity (%), volume of pores (cm3), total volume (cm3) | Calculate the porosity of a rock |
| Permeability = (fluid flow rate / pressure gradient) x (fluid viscosity / rock thickness) | Permeability (m2), fluid flow rate (m3/s), pressure gradient (Pa/m), fluid viscosity (Pa·s), rock thickness (m) | Calculate the permeability of a rock |
Common Queries
What are the primary geological processes that shape rocks?
Weathering, erosion, and deposition are the fundamental processes responsible for transforming and reshaping rocks.
How are rocks classified based on their composition and texture?
Rocks are categorized into three main types: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic, each exhibiting distinct characteristics based on their formation processes.
What are the key physical and chemical properties of rocks?
Density, porosity, and permeability are crucial properties that influence rock behavior and determine their suitability for various geological applications.
What types of rock structures exist, and how do they form?
Folds, faults, and joints are common rock structures resulting from tectonic forces and geological processes.
What is the significance of rock equations in geology?
Equations provide mathematical tools to calculate rock properties, relationships, and behavior, aiding in geological modeling and understanding.