Human torso model with labels – Step into the fascinating world of human anatomy with our comprehensive guide to human torso models with labels. These models provide an invaluable tool for visualizing and understanding the intricate structures of the human body, making them indispensable in medical education, art, and beyond.
Join us as we delve into the anatomical landmarks of the human torso, explore their medical applications, and discover the role they play in education and artistic representation. We’ll also provide practical guidelines for labeling and annotating these models, ensuring effective communication of anatomical information.
Anatomical Structure
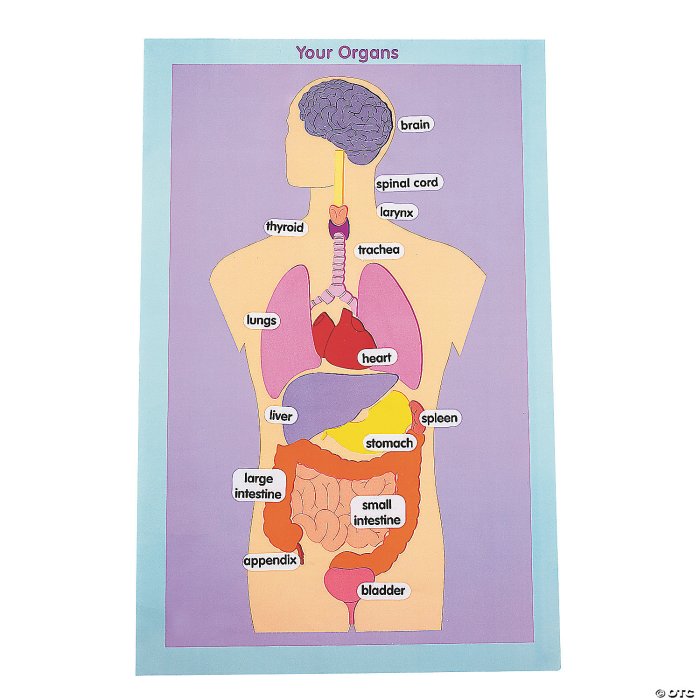
The human torso is a complex and fascinating structure, consisting of multiple regions, each with its own unique anatomical features. These regions include the head, neck, chest, abdomen, and pelvis. Understanding the key anatomical landmarks of each region is essential for comprehending the human body’s structure and function.
The head is the uppermost region of the torso and houses the brain, the control center of the nervous system. The skull, a bony structure, encloses and protects the brain. The face, located at the front of the head, contains the eyes, nose, mouth, and ears, which are responsible for sensory perception.
The neck, a relatively short and flexible region, connects the head to the rest of the torso and allows for movement of the head.
The chest, also known as the thorax, is located below the neck and is enclosed by the ribs and sternum. It contains the heart, lungs, and other vital organs. The heart, a muscular organ, pumps blood throughout the body, while the lungs are responsible for gas exchange.
The abdomen, situated below the chest, is the largest region of the torso and contains the stomach, intestines, liver, and other digestive organs. The pelvis, the lowermost region of the torso, is formed by the hip bones and sacrum. It supports the weight of the body and houses the reproductive organs.
Skeletal Structure
The skeletal structure of the torso provides support, protection, and facilitates movement. The skull, ribs, sternum, and vertebrae form the bony framework of the torso. The skull consists of 22 bones that protect the brain and provide attachment points for muscles.
The ribs, 12 pairs in total, form the rib cage, which encloses and protects the heart and lungs. The sternum, a flat bone located at the front of the chest, connects the ribs and provides attachment points for muscles.
The vertebrae, 33 in total, form the spinal column, which extends from the skull to the pelvis. The spinal column provides support, protects the spinal cord, and allows for movement. The pelvis, formed by the hip bones and sacrum, provides attachment points for muscles and supports the weight of the body.
Muscles
The muscles of the torso are responsible for movement, posture, and protection. The head and neck muscles allow for movement of the head, facial expressions, and swallowing. The chest muscles, including the pectoralis major and minor, are responsible for breathing and arm movements.
The abdominal muscles, including the rectus abdominis, obliques, and transverse abdominis, support the spine, protect the abdominal organs, and aid in breathing.
The pelvic muscles, including the gluteus maximus, hamstrings, and quadriceps, are responsible for hip and leg movements. These muscles work together to provide stability, mobility, and protection to the torso.
Major Organs, Human torso model with labels
The torso houses several major organs, each with its own vital functions. The brain, located within the skull, is the control center of the nervous system and responsible for thought, emotions, and movement. The heart, situated in the chest, pumps blood throughout the body, supplying oxygen and nutrients to cells and removing waste products.
The lungs, also located in the chest, are responsible for gas exchange, taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide. The stomach, intestines, liver, and pancreas, located in the abdomen, are responsible for digestion and absorption of nutrients. The kidneys, located near the middle of the back, filter blood and produce urine.
The reproductive organs, located in the pelvis, are responsible for reproduction. The male reproductive organs include the testes, which produce sperm, and the penis, which is responsible for delivering sperm during sexual intercourse. The female reproductive organs include the ovaries, which produce eggs, and the uterus, where a fertilized egg implants and develops into a fetus.
Medical Applications
Human torso models serve as invaluable tools in the realm of medical education and training. They provide a tangible and three-dimensional representation of the human body, enabling students and medical professionals to visualize and comprehend the intricate complexities of human anatomy.
Through the use of these models, students can gain a thorough understanding of the relationships between different organs, muscles, and bones. This knowledge is essential for developing a solid foundation in anatomy, which is crucial for diagnosing and treating various medical conditions.
Educational Use
- Interactive Learning:Torso models allow students to actively engage with the material, enabling them to manipulate and examine the structures from various angles.
- Visual Aids:The three-dimensional representation of the body provides a more vivid and memorable learning experience compared to traditional textbooks or diagrams.
- Assessment Tool:Educators can utilize torso models to assess students’ understanding of anatomical concepts through practical examinations.
Professional Training
- Surgical Preparation:Surgeons use torso models to plan and practice complex surgical procedures, minimizing the risk of complications during actual surgeries.
- Patient Education:Models aid in explaining medical conditions and treatment options to patients, enhancing their understanding and fostering better communication.
- Research and Development:Researchers employ torso models to develop new medical devices and techniques, advancing the field of medicine.
Educational Resources
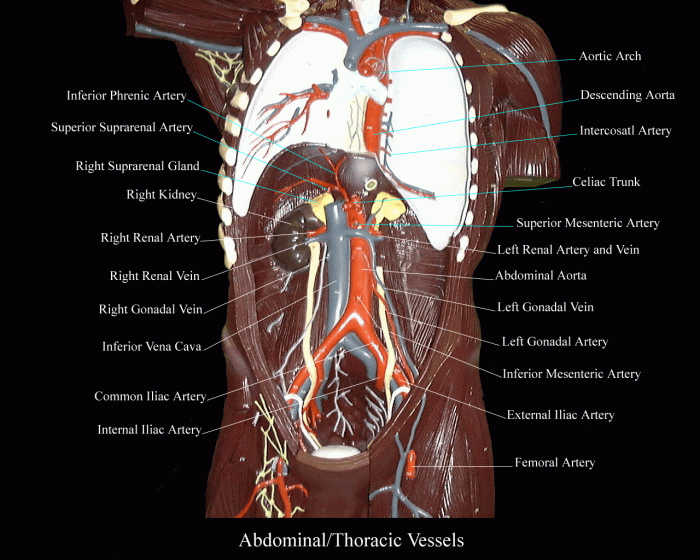
Human torso models are valuable tools in education, providing students with a tangible representation of the human body’s complex anatomy. These models facilitate a comprehensive understanding of the structures, organs, and systems within the torso.
Various educational materials incorporate human torso models, including:
Textbooks
Textbooks often include detailed illustrations and diagrams of human torso models, providing a static reference for students. While these models lack the interactivity of other resources, they offer a comprehensive overview of anatomical structures.
Interactive Simulations
Interactive simulations allow students to explore human torso models in a dynamic environment. These simulations enable students to manipulate models, zoom in on specific structures, and visualize anatomical relationships in a more engaging way.
Online Resources
Numerous online resources provide access to human torso models, including interactive 3D models and virtual dissection simulations. These resources offer a convenient and accessible way for students to learn about human anatomy from anywhere with an internet connection.
The use of human torso models as teaching aids offers several benefits:
- Enhanced visualization: Models provide a tangible representation of the human body, improving students’ understanding of anatomical structures and their spatial relationships.
- Interactive learning: Interactive models allow students to explore anatomical structures in a hands-on manner, promoting active learning and deeper comprehension.
- Supplements textbooks: Models complement textbooks by providing a visual representation of the concepts being discussed, reinforcing learning and improving retention.
However, it’s important to note the limitations of using human torso models:
- Accuracy: Models may not always accurately represent the variability of human anatomy, which can lead to misconceptions if not used in conjunction with other resources.
- Cost: High-quality models can be expensive, limiting their accessibility in some educational settings.
- Limited interactivity: While interactive models offer more interactivity than static models, they may not fully replicate the experience of dissecting a real human body.
Overall, human torso models are valuable educational resources that can enhance students’ understanding of human anatomy. By incorporating these models into educational materials, educators can provide students with a more engaging and comprehensive learning experience.
Artistic Representation
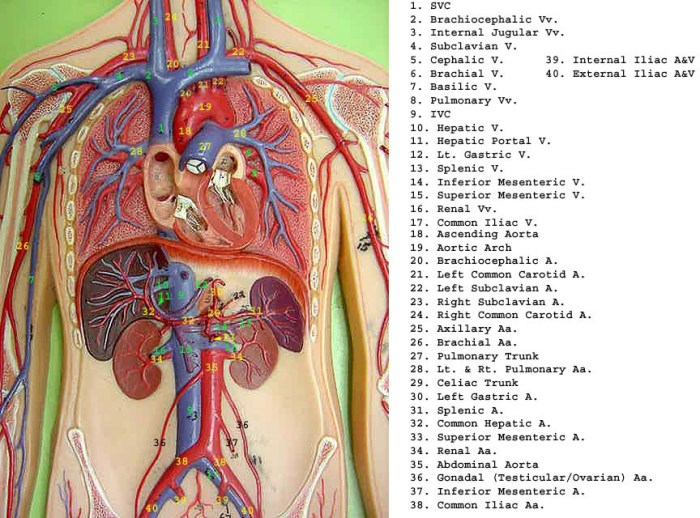
Human torso models have played a significant role in the realm of art and design, serving as invaluable tools for artists seeking to create anatomically accurate and realistic representations of the human form.
These models provide a comprehensive understanding of the human body’s structure and proportions, enabling artists to capture the nuances of musculature, bone structure, and surface anatomy. They are particularly crucial in disciplines such as figure drawing, sculpture, and anatomy for artists.
3D Models and Digital Sculpting
In recent years, the advent of 3D modeling software and digital sculpting techniques has revolutionized the use of human torso models in art. Artists can now create highly detailed and realistic digital models of the human body, allowing for precise control over anatomy and posing.
Studying the human torso model with labels is a great way to learn about the different parts of the body. For more in-depth knowledge, you can check out wordly wise book 5 lesson 11 , which provides detailed information and exercises on body parts.
The human torso model with labels is an excellent tool for students and anyone interested in human anatomy.
These models are widely used in the entertainment industry, particularly in the creation of video games, animated films, and other digital media. They enable artists to create lifelike characters with accurate anatomy and movement.
Types of Models
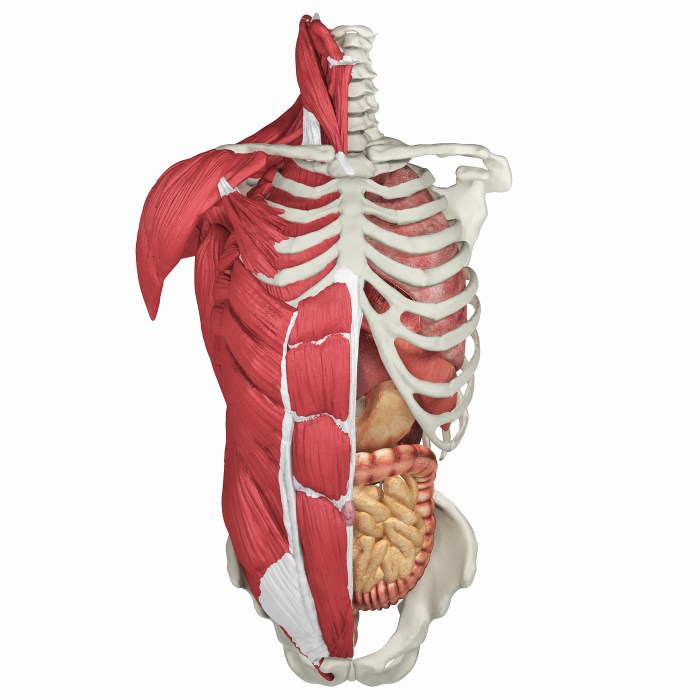
Human torso models vary in materials, features, and applications. Understanding the different types can help you choose the most suitable model for your specific needs.
The following table compares the common types of human torso models:
| Type | Materials | Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic Models | Durable plastic | Lightweight, affordable, basic anatomical structures | Basic anatomy education, patient education |
| Foam Models | Lightweight foam | Soft, flexible, allows for manipulation of organs | Interactive learning, surgical training |
| Anatomical Models | Realistic materials (e.g., silicone, latex) | Highly detailed, lifelike representation of anatomical structures | Advanced medical training, research |
| Virtual Models | Computer-generated images | Interactive, customizable, can be manipulated in 3D | Virtual surgery simulations, medical education |
Specific examples of each type include:
- Plastic Model:Visible Human Body Torso Model by 3B Scientific
- Foam Model:Life/form Torso with Removable Organs by Nasco
- Anatomical Model:Erler Zimmer Human Torso Model by 3B Scientific
- Virtual Model:Anatomage Table by Anatomage
Labeling and Annotation
Accurate labeling and annotation of human torso models are crucial for educational purposes. They provide learners with a clear understanding of anatomical structures and their functions, facilitating effective learning and retention.
When creating labels, it is essential to ensure they are clear, concise, and accurate. They should use precise anatomical terminology and provide a brief description of the structure’s function. For example, the label for the “heart” could read: “Heart: Pumps blood throughout the body.”
Guidelines for Effective Labeling
- Use precise anatomical terminology.
- Provide a brief description of the structure’s function.
- Use a consistent font and size for all labels.
- Place labels close to the anatomical structures they represent, without obscuring them.
- Consider using different colors or symbols to differentiate between different types of structures (e.g., bones, muscles, organs).
3D Visualization: Human Torso Model With Labels
3D visualization techniques revolutionize the creation of human torso models, offering interactive and immersive experiences that greatly enhance the learning of human anatomy.
These models allow users to rotate, zoom, and dissect virtual human torsos, providing a comprehensive understanding of the anatomical structures, their relationships, and their functions. Unlike traditional 2D images, 3D models enable students to visualize complex structures from multiple angles, fostering a deeper comprehension of the human body.
Interactive Learning
Interactive 3D models empower students to actively engage with the learning material. They can manipulate the models, isolate specific structures, and explore anatomical relationships in a dynamic and engaging manner. This hands-on approach enhances understanding and retention, making the learning process more effective and enjoyable.
Immersive Experience
3D visualization techniques create immersive experiences that transport students into the human body. They can virtually dissect structures, examine internal organs, and navigate through complex anatomical pathways. This immersive environment fosters a deeper connection with the subject matter, promoting a more comprehensive understanding of human anatomy.
Answers to Common Questions
What are the benefits of using human torso models with labels?
Human torso models with labels provide numerous benefits, including enhanced visualization of anatomical structures, improved understanding of their functions and relationships, and a convenient reference for studying and teaching human anatomy.
What are the different types of human torso models available?
Human torso models come in various types, including full-body models,半身 models, and organ-specific models. They can be made from materials such as plastic, resin, or silicone, and may feature different levels of detail and accuracy.
How can I effectively label and annotate human torso models?
Effective labeling and annotation involve using clear and concise terminology, placing labels in appropriate locations, and providing accurate descriptions of anatomical structures and their functions. Consider using different colors or fonts to highlight important structures or relationships.